Cropping images#
When working with microscopy images, it often makes limited sense to process the whole image. We typically crop out interesting regions and process them in detail.
from skimage.io import imread, imshow
image = imread("../../../data/blobs.tif")
Before we can crop an image, we may want to know its precise shape (dimensions):
image.shape
(254, 256)
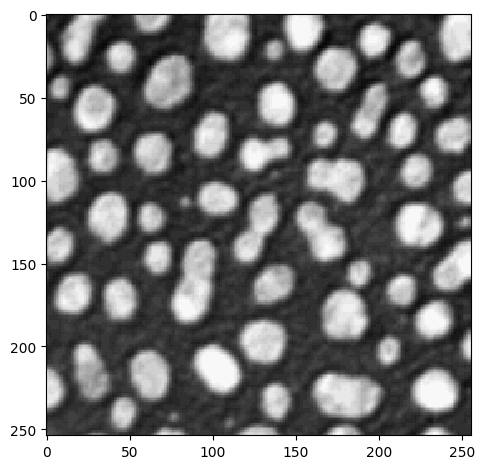
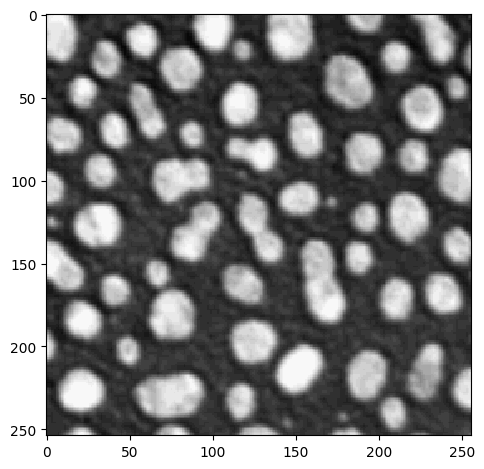
Recap: Visualization using imshow:
imshow(image)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x219cf257490>
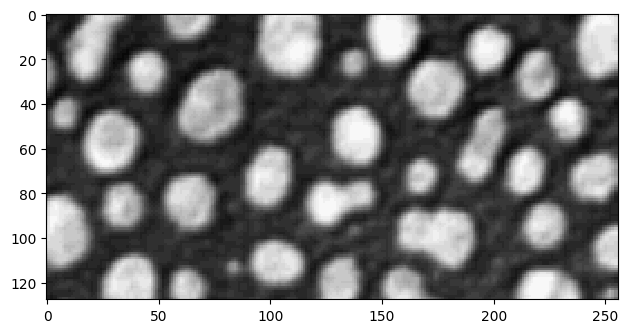
Cropping images works exactly like cropping lists and tuples:
cropped_image1 = image[0:128]
imshow(cropped_image1)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x219cf20e0e0>
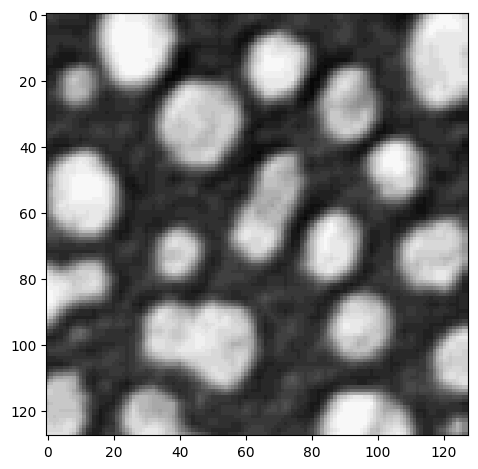
To crop the image in the second dimension as well, we add a , in the square brackets:
cropped_image2 = image[0:128, 128:]
imshow(cropped_image2)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x219d05257e0>
Sub-sampling images#
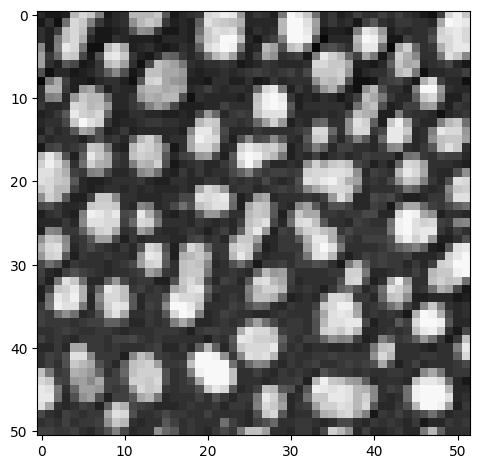
Also step sizes can be specified as if we would process lists and tuples. Technically, we are sub-sampling the image in this case. We sample a subset of the original pixels:
sampled_image = image[::5, ::5]
imshow(sampled_image)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x219d0593490>
Flipping images#
Negative step sizes flip the image.
flipped_image = image[::, ::-1]
imshow(flipped_image)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x219d05f7cd0>
Exercise#
Open the banana020.tif data set and crop out the region where the banana slice is located.
